courtesy of Wikipedia
B&R rig
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigationJump to search
A variant of the Bermuda sailboat rig
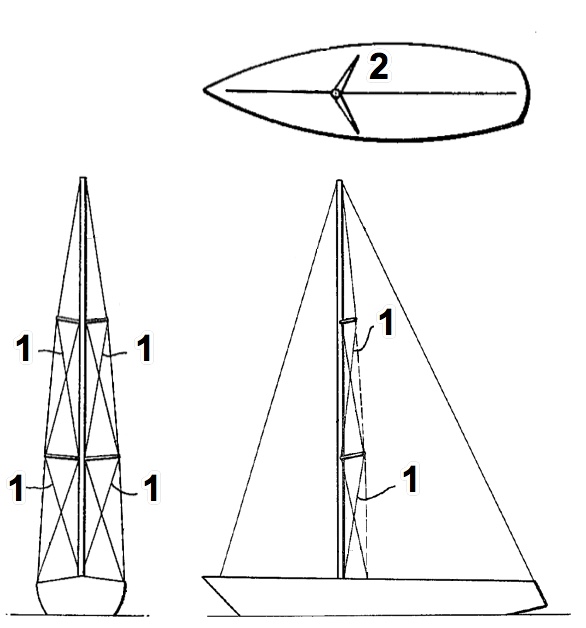
Characteristics of the B&R rig include swept spreaders (2) and reverse-diagonal shrouds (1).
The
B&R rig is a variant of the
Bermuda sailboat
rig, designed and patented by Swedish aeronautical engineers
Lars Bergström and
Sven Ridder.
[1] It employs swept
spreaders that are usually angled aft, together with "stays" running diagonally downward from the tip of the spreaders to the attachment of the next pair of spreaders to the
mast or to the intersection of the mast with the
deck (so-called reverse-diagonal shrouds) that facilitates a pre-bend of the mast (curving aft) that is sometimes
tuned into the rig before it is stepped onto the boat. Conventional
shrouds thereby contribute to both lateral and longitudinal stability, unlike rigs with unswept spreaders.
[2] A B&R rig can be a
masthead or
fractional rig depending on how
stays are configured;
[3] a
backstay is optional.
[4] Such rigs are employed in many of the models of at least one U.S. manufacture and in many thousands of boats, worldwide.
[4][5]
Contents
History[edit]
The earliest B&R rig was the result of wind tunnel tests and research by Lars Bergstrom and Sven Ridder at Sweden's
Royal Institute of Technology.
[6] The first generation, built around 1970, included a
backstay and was used on many production boats. A patent application for the B&R rig was submitted in 1973 and was granted in 1975.
[1] A second generation eliminated the backstay but used solid, deck-mounted struts to brace the lower mast section. In 1982 a second generation B&R rig with 2 forestays was incorporated into the 60 ft (18.3 m) "breakthrough" racing yacht
Thursday's Child. On February 13, 1989
Thursday's Child beat the 135 year old clipper ship record sailing 15,000 mi (24,140 km) from New York to San Francisco.
[7] A third generation B&R rig mounted the mast on a tripod of struts, had a single forestay and no backstay. In 1993 the third generation was incorporated into the all carbon/kevlar 68 ft (20.7 m) yacht
Route 66.
[6][8][9][10] The 60 ft (18.3 m) yacht
Hunter's Child finished 2nd in the
1994-95 BOC Challenge using a 2nd Generation B&R rig. By 1997 more than 10,000 production sailboats were using the B&R rig.
[4][11]
Tuning[edit]
Part of the design of the B&R rig involves inducing a "pre-bend" in the mast which provides some of the side-to-side and fore-and-aft stability of the rig.
[2][3][4] The pre-bend is achieved by tensioning the reverse diagonals and certain other so called intermediate shrouds. Because the spreaders are swept back at approximately a 25° to 30° angle, this tensioning bows the mast. Balanced and proper tensioning keeps the bow in the mast in the fore-aft direction and eliminates any curvature in the sideways direction. The pre-bend is generally set up on the ground before the mast is stepped (placed onto the boat). The mast is then stepped and all other
standing rigging is attached to the boat and properly tensioned.
[4][6][12]
Boat and yacht models incorporating B&R rigs[edit]
The majority of
Hunter Marine's fleet incorporated the B&R rig. However, manufacturers on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean have employed B&R rigs in their boat designs.
hide
Models with 1st Generation B&R rigs |
|---|
| Boatbuilder | Model | 1st Year Produced | Last Year Produced | Ref |
|---|
| Hunter Marine | | 1983 | 1987 | | | Hunter Marine | | late 1982 | 1987 | | | Hunter Marine | Passage 42 | 1989 | 1998 | | | AB Radab | Windex 92 | 1981 | 1991 | |
|
hide
Models with 2nd Generation B&R rigs |
|---|
| Boatbuilder | Model | 1st Year Produced | Last Year Produced | Ref |
|---|
| Hunter Marine | 420 | 1998 | 2004 | | | Hunter Marine | Passage 450 | 1996 | | | | Hurley Marine Ltd. (UK) | Tailwind 38 | 1973 | 1974 | | | Torkel Batar (Sweden) | | 1993 | - | |
|
hide
Models with 3rd Generation B&R rigs |
|---|
| Boatbuilder | Model | 1st Year Produced | Last Year Produced | Ref |
|---|
| Goetz Custom Sailboats | Route 66 | 1993 | | |
|